The YSZ (yttria-stabilized zirconia) coating was developed for titanium abutments in dental prostheses to enhance aesthetics and reduce potential allergic reactions. Applied through reactive magnetron sputtering deposition via the PVD-PECVD Centurion system, the YSZ coating improves biocompatibility while maintaining durability. This innovation addresses both aesthetic concerns and allergic reactions, making titanium abutments suitable for a wider range of patients. The YSZ coating is a few hundred nanometers thick and features a stable, defect-free cubic zirconia structure. It remains intact even after low-temperature degradation testing, simulating 75 years of exposure in the oral environment. The translucent yellow color of the coating minimizes gingival discoloration, giving the prosthesis a more natural appearance compared to untreated titanium. This advanced solution provides significant improvements in both the functionality and appearance of titanium dental abutments.
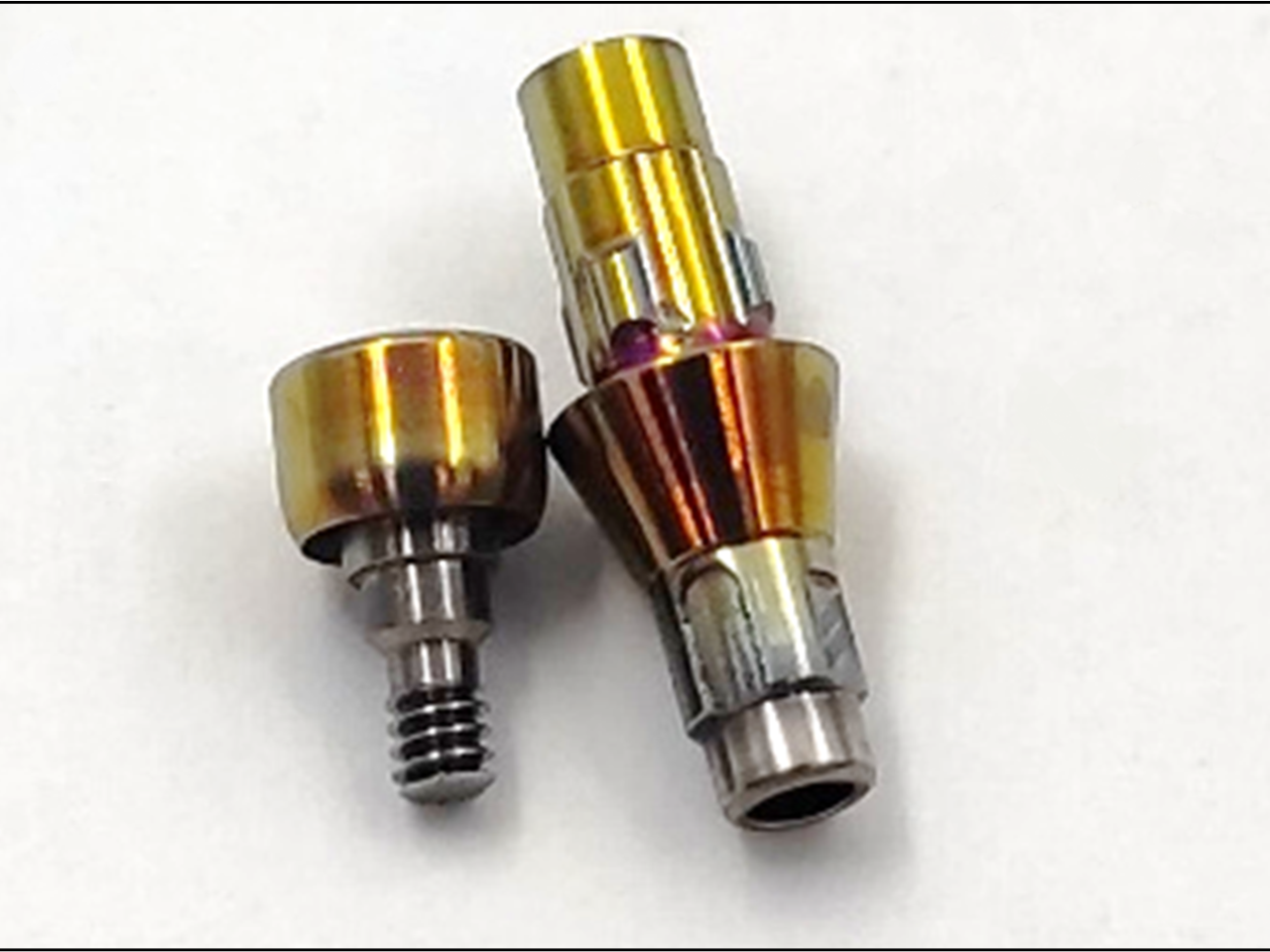 YSZ coating on abutments
YSZ coating on abutments
The YSZ (yttria-stabilized zirconia) coating is designed for patients who cannot afford a full zirconia prosthesis but still require high aesthetics and a hypoallergenic solution. Applied to titanium abutments, it provides a natural look while eliminating potential allergic reactions caused by direct titanium exposure. This makes it a practical alternative for a wider range of patients, ensuring both affordability and performance. The deposition process is highly efficient, as multiple abutments are coated at once, lowering costs without sacrificing quality.
Serving as a protective barrier, the YSZ coating prevents aesthetic concerns like gingival discoloration while enhancing biocompatibility. Its defect-free, translucent yellow cubic zirconia structure blends seamlessly with surrounding tissues, offering a visually appealing and durable solution. Additionally, the coating enhances the long-term stability of titanium abutments, reducing the risk of surface degradation and ensuring reliable integration with prosthetic components. This innovative approach makes high-quality dental solutions more accessible without compromising essential functional and aesthetic benefits.
The innovative aspect of this project lies in the deposition of a coating that not only mimics the natural appearance of gingival tissue but also eliminates allergic risks associated with titanium. Unlike conventional surface treatments such as titanium anodization, which offers limited aesthetic improvements, this coating provides a more effective and lasting solution by fully masking the titanium surface while maintaining biocompatibility.
Another key innovation is the deposition method itself. Few utilize reactive sputtering deposition, a technique that allows highly precise control over the properties of the coating. This advanced process ensures a defect-free, stable cubic zirconia structure with the desired translucency and color, optimizing both performance and appearance. By combining aesthetic enhancement with superior material control, this approach represents a significant advancement in dental prosthetic technology.
The YSZ (Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia) coating is applied in the medical field to functionalize the abutment surface of dental prostheses, enhancing their biocompatibility and aesthetic appearance. This coating is particularly useful in oral applications for replacing missing teeth and can be deposited on various types of abutments, such as healing and Variobase types. The wide coverage application depends on the specific deposition system chosen, allowing the YSZ coating to be applied without being affected by geometric variations, ensuring consistent quality and performance.
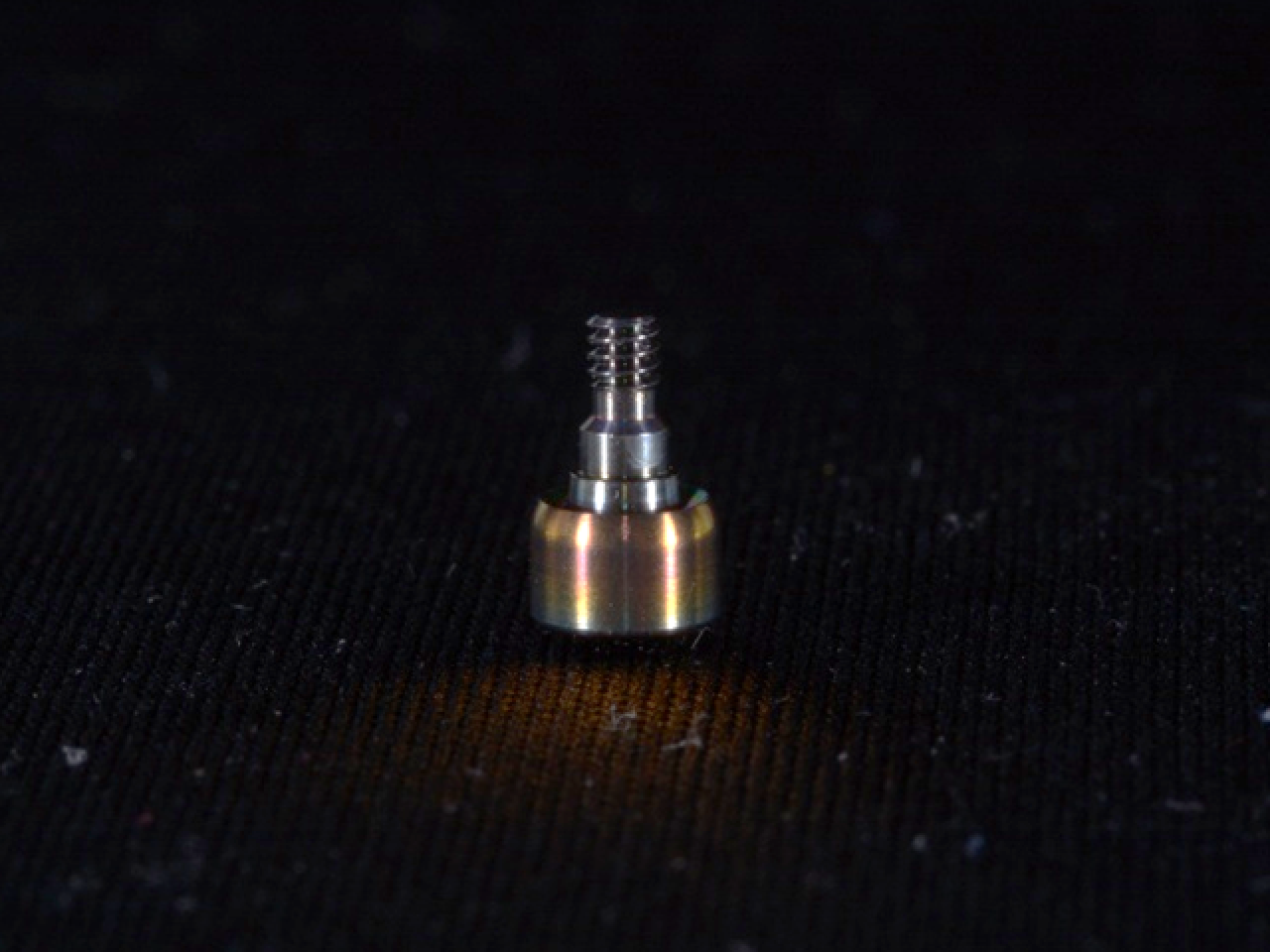 YSZ coating on healing abutment
YSZ coating on healing abutment
YSZ coating for dental prosthesis abutments: enhancing aesthetic appearance and preventing allergic reactions in medical oral applications for replacing missing teeth
Further in vivo studied are required
The project was a collaboration between Il Sentiero International Campus and the University of Modena, specifically involving the engineering department (DIEF) and the Modena Polyclinic.
Further in vitro and in vivo tests are required for the patent, specifically in the biomedical field. These tests include in vitro experiments with cells and in vivo studies for implant validation. The involved partners are also essential for enhancing the product's value.
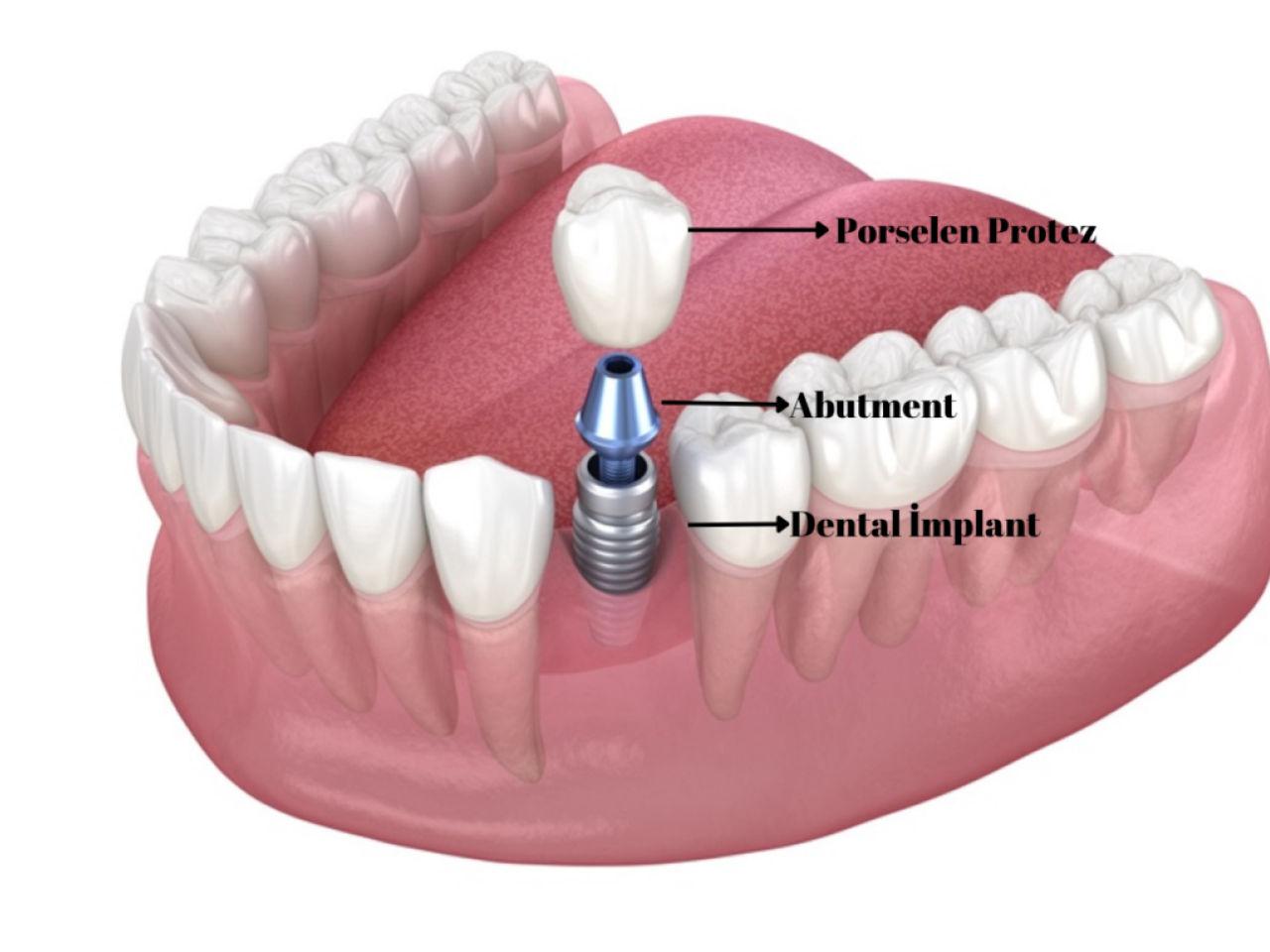 dental prosthesis application
dental prosthesis application

