Niobium carbide (NbC) has long been employed to produce bulk hardmetals, e.g. for cutting tools, but practically it has not been investigated as coatings. This contribution provides an overview of our research with NbC-based coatings with Ni- and Fe-based matrices. The feedstock materials were prepared by High-Energy Ball Milling (HEBM) due to this process's flexibility and scalability, which yields rounded particles containing a uniform distribution of fine NbC grains. The coatings were obtained by H2-fuelled High-Velocity Oxygen-Fuel (HVOF) spraying.
NbC-NiCr formulations exhibit a good combination of room-temperature and intermediate-temperature (200°C) sliding wear resistance, tested by the ball-on-disc method, and excellent corrosion resistance in aqueous 3.5% NaCl. NbC-40vol.%FeCrMo is more brittle and less sliding wear-resistant at room temperature, but it exhibits excellent wear resistance at 400°C due to the formation of a protective tribo-oxidized “glaze”.
 HVOF gun - Diamond Jet 2600 system
HVOF gun - Diamond Jet 2600 system
Three compositions of NbC-based coatings, specifically: NbC-25vol.%(Ni-20wt.%Cr), NbC-40vol.%(Ni-20wt.%Cr) and NbC-40vol.% (Fe-wt.%25Cr-wt.%15Mo) were produced by High-Velocity Oxygen-Fuel (HVOF) spraying onto AISI 304 stainless steel plates using a Diamond Jet 2600 HVOF hybrid torch.
After the thermal spraying, the coated samples were characterized by microstructural analysis (SEM), determination of the Vickers microhardness, dry sliding behaviour and electrochemical corrosion resistance. Their performances were compared to WC-CoCr and Cr3C2-NiCr (conventional carbide coatings) under different wear and corrosion conditions.
Considering the absence in the literature of research carried out with NbC-based hardmetal coatings sprayed by High-Velocity Oxygen-Fuel (HVOF), especially using NiCr and FeCrMo as binders, this research is innovative by characterizing the properties of new compositions of hardmetal coatings.
Among conventional carbide coatings, WC-CoCr stands out for its high wear resistance and Cr3C2-NiCr for its good performance under high-temperature oxidative environments. However, WC-CoCr is unsuitable for high-temperature applications (thermal expansion incompatibility, oxidation), while Cr3C2-NiCr offers less wear protection at low and moderate temperatures. Thus, niobium carbide-based coatings are promising alternatives for applications that require a balance of wear resistance and corrosion, and/or for applications at intermediate and high temperatures (200 to 600 °C).
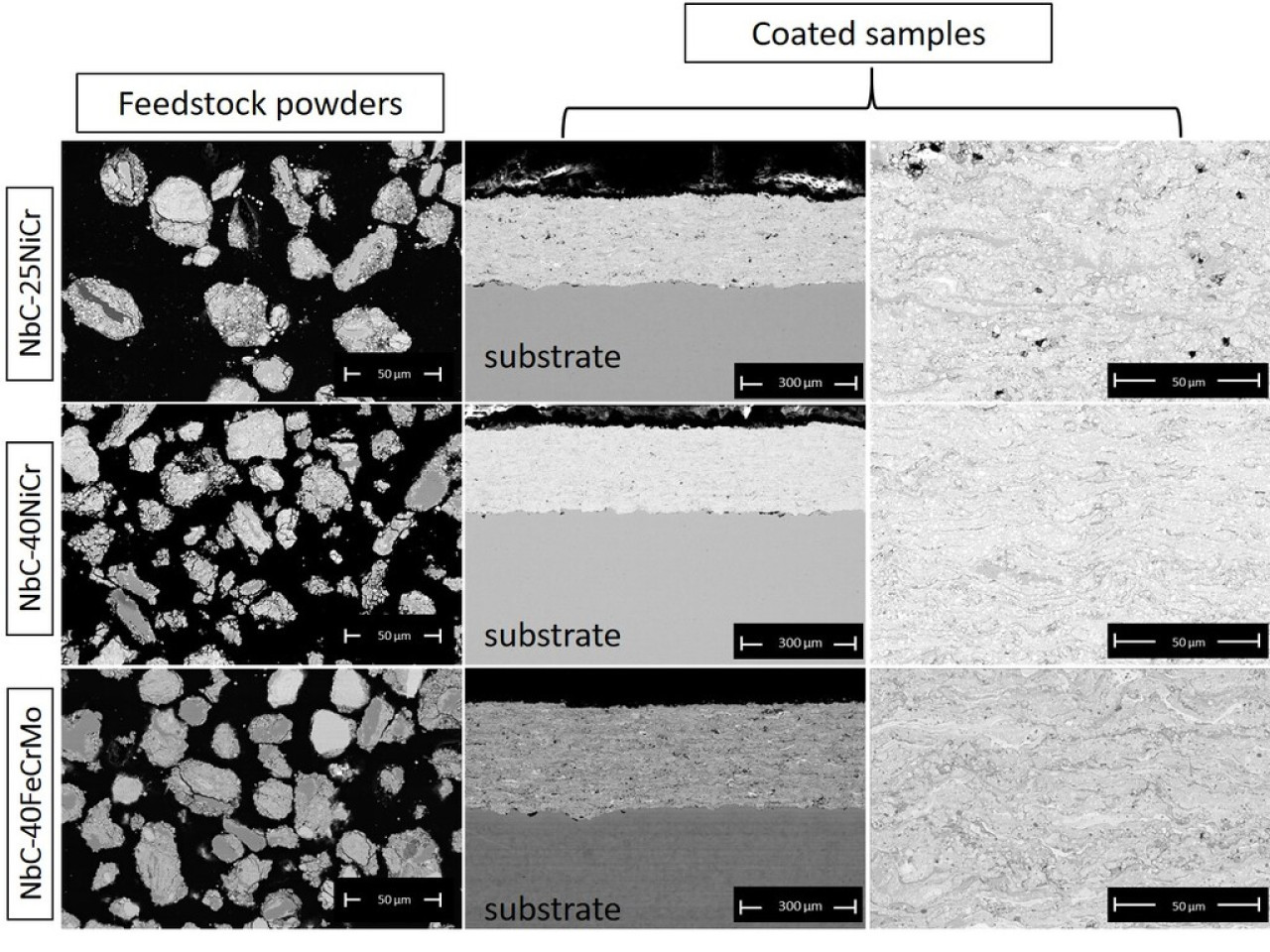 SEM micrographs of feedstock powders and of the cross-section HVOF-sprayed NbC-based coatings
SEM micrographs of feedstock powders and of the cross-section HVOF-sprayed NbC-based coatings
Despite the research is still ongoing and testing to validate commercial-level applicability has not been performed, thermally sprayed coatings generally provide wear and corrosion protection in a variety of applications like ball valves, papermaking and steelmaking rolls, hydraulic turbine parts, pump parts, hydraulic rods, etc.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and Vickers microindentation analyses revealed that all NbC-based coating compositions have low porosity (<1%) and microhardness in a range of 900 – 1000 HV0.3 respectively.
The ball-on-disc setup (10 N test load, 0.4 m/s sliding speed and 3 mm Ø - WC-6Co and Al2O3 ball counterpart) was used to determine the dry sliding wear resistance of the samples at room temperature, 200°C, 400°C and 600°C. The wear rates of the NbC-25NiCr and NbC-40NiCr compositions progressively increased with increasing temperature, while the NbC-40FeCrMo showed significantly lower wear rates at 400 °C and 600 °C. The values obtained showed that the NbC-NiCr coatings are a promising technology to obtain intermediate and balanced performances between the conventional WC-CoCr and Cr3C2-NiCr coatings and the NbC-FeCrMo coating for sliding wear applications at 400 – 600 °C.
In terms of corrosion resistance, the NbC-NiCr compositions exhibit a very promising performance concerning the reference coatings and are more corrosion resistant and more noble compared to the WC-CoCr coating. The NbC-40NiCr composition particularly stands out for having better corrosion resistance than the conventional Cr3C2-NiCr coating, approaching the performance of polished AISI 304 stainless steel.
UNIMORE, MBN Nanomaterialia and CBMM – Companhia Brasileira de Metalurgia e Mineração.
Development and research of alternative compositions to conventional carbide coatings (WC-CoCr and Cr3C2-NiCr).
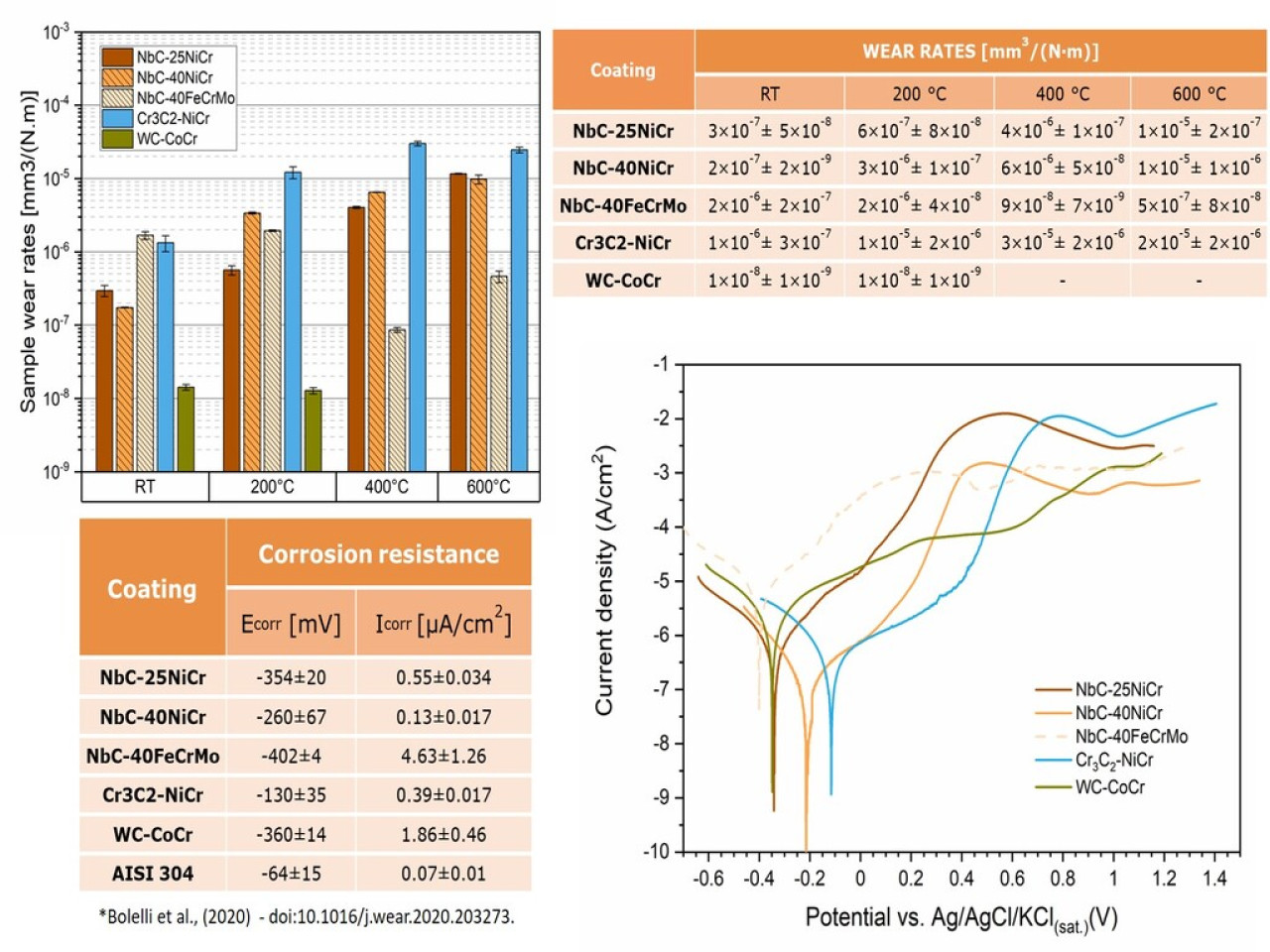 Ball-on-disk dry sliding wear rates and electrochemical polarization curves of coated samples and reference coatings.
Ball-on-disk dry sliding wear rates and electrochemical polarization curves of coated samples and reference coatings.

