Micronozzle is a device that allow the fabrication of flexible tube made of polymeric material obtained by extrusion. The tubes are made by extrusion of a polymer melt forced to pass through a suitable nozzle size equal to the section of pipe that is to be realized. The devices is realized in silicon and it has been developed and fabricated in collaboration with the CNR-IMM institute of Bologna. It consists of a reservoir, with a constant volume of about 2 microliter, which connect the inlet, where the pressurized molten polymer enters, and a micronozzle. We focus at companies operating in the biomedical field, already operating in the market for dialysis filters and wish to innovate by exploiting a new technology for the production of extruded polymeric materials, or that are going to get into that market.
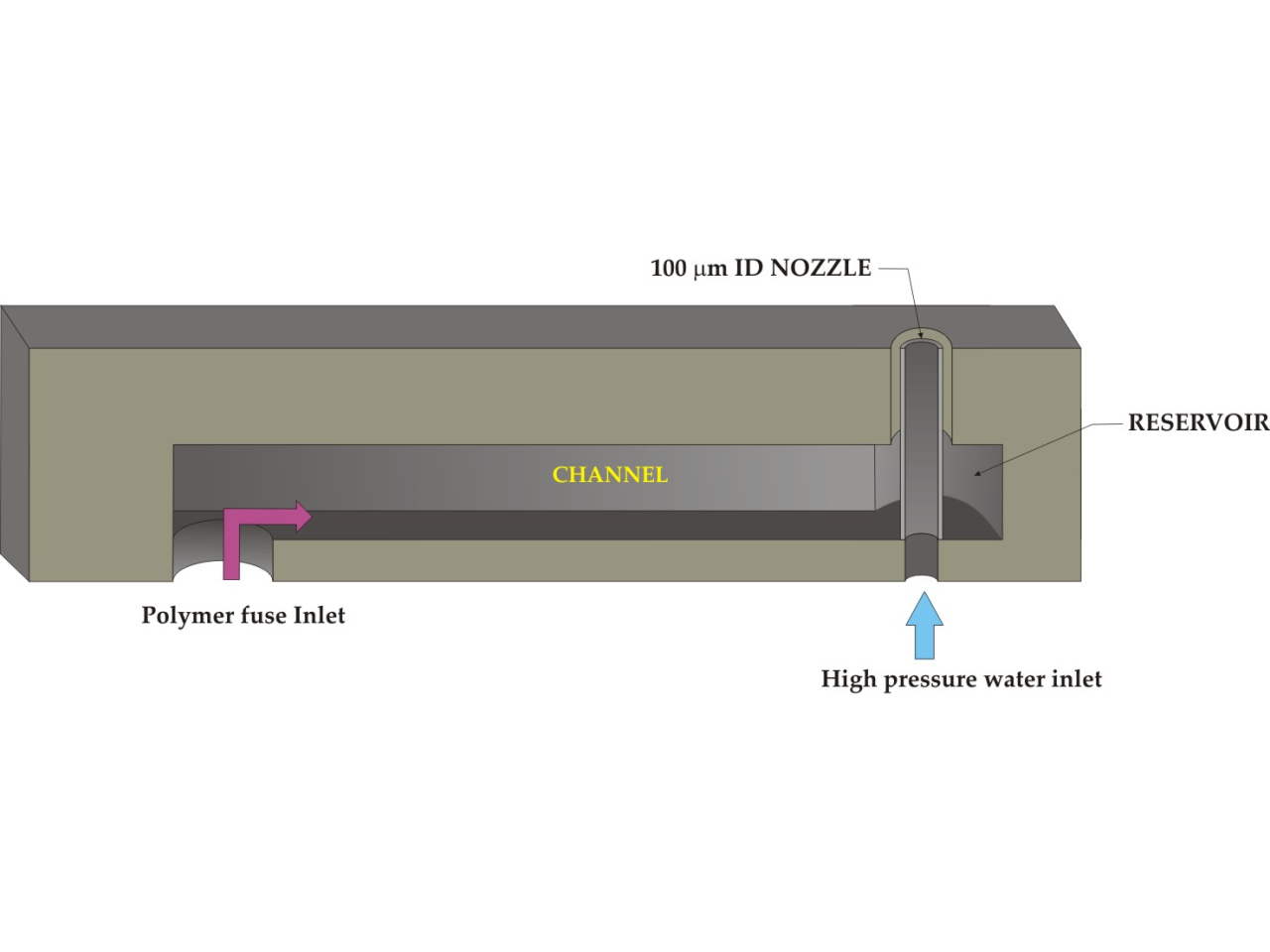 Principle of a micronozzle
Principle of a micronozzle
The proposed technology exploits the potential offered by the MEMS technology for the manufacture of miniaturized devices with high precision, reliability and compactness. Currently commercial nozzle used for the manufacture of micrometric pipes of polymer material are made of metal and manufactured a high-precision mechanical technology. MEMS technology allows to achieve accuracies of at least one order of magnitude higher compared to the most advanced micromechanics technology. Moreover, the proposed technology allows the realization of micrometric nozzle self-aligned, with a precision of a few micrometers. The size of the nozzle, which determines the section of the capillary tube may vary from a few tens of microns up to millimeter dimensions according to the applications for which it is used. The device can be designed and manufactured according to the requirements.
A potential application is in medical applications and in the present case in the realization of capillary filters for hemodialysis.
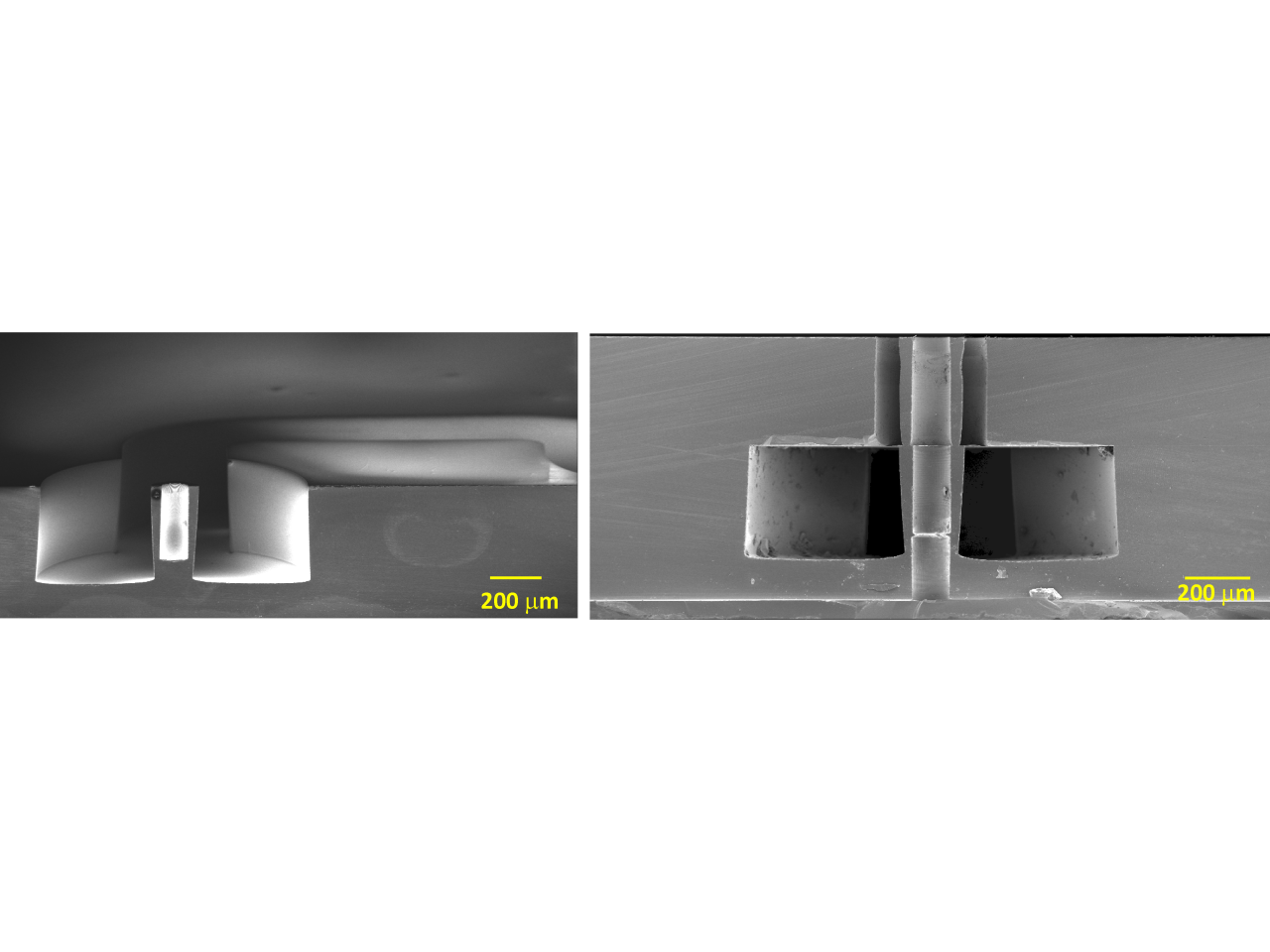 Cross-section SEM image of a all-silicon micronozzle silicon fabricated by MEMS technology
Cross-section SEM image of a all-silicon micronozzle silicon fabricated by MEMS technology
Realization of flexible polymeric tubes of micrometer size for the manufacture of dialysis filters
The device consists substantially in a chamber with a known volume, from an input pressurized microfluidic channel and from a micronozzle with an inner diameter of 100 um. The molten polymer is forced, by a pneumatic system, in the outer region of the nozzle and at the same time, during the extrusion, flowing in the internal region of the water nozzle at high pressure that activates the polymerization of the material. The proposed device has been tested on a commercial machine to replace mechanical system currently in use, without extensive modification of the physical parameters. The first results obtained in the field with micronozzle silicon are very promising. Some physical parameters, such as pressure and temperature of the molten polymer, must be optimized.
Medica S.p.A
The micronozzle showed an extreme mechanical robustness during the tests for the development of the extrusion process. A compatible geometry of the entire device and the fluidic inputs compared to steel commercial product has made it simple to replace the commercial machine.
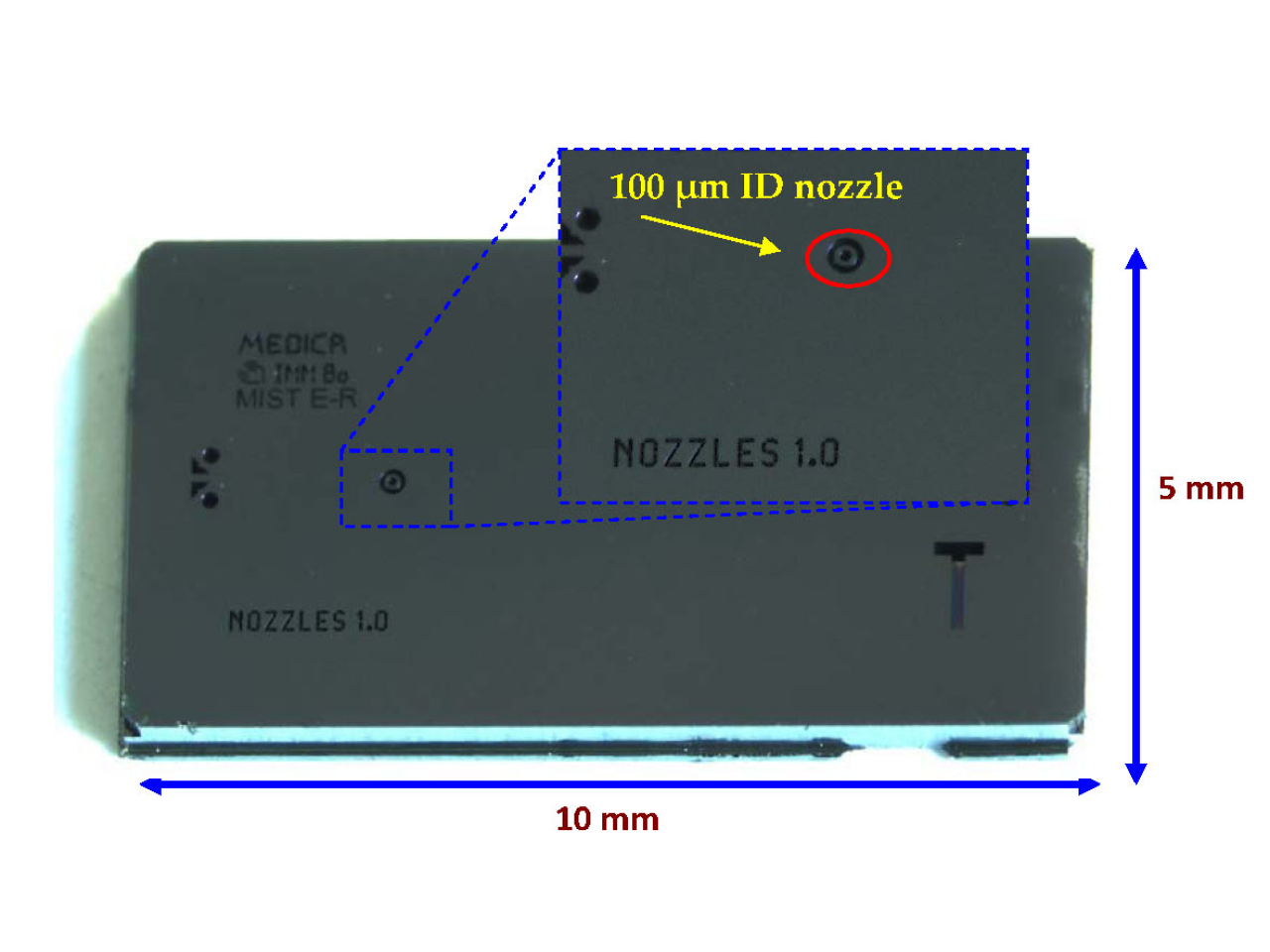 Optical image of a complete all-silicon micronozzle
Optical image of a complete all-silicon micronozzle

