To contribute to identify the most effective choices towards a sustainable waste management, the MatER Study Center provides technical and scientific consultancy based on a thorough survey of the technologies and policies adopted for recovering materials and energy from waste. All that through: Analysis of best practices and implementation of studies and researches on recovering materials and energy from waste; Review and improvement of the regulations on waste management, recovery and treatment; Gathering, spreading and sharing correct information on the issue of waste management, also by organising courses and seminars. The MatER Study Center, set up by the LEAP Consortium with the support of Federambiente and of the largest multi-utilities operating in Italy in the environmental hygiene sector, aims at being a go-to scientific partner in the sector of recovering materials and energy from waste at national level.
 MatER Study Center of the LEAP Laboratory
MatER Study Center of the LEAP Laboratory
Promotion of sustainable waste management strategies and policies, to contribute to define treatment and management techniques, according to sustainability guidelines. The research and the scientific divulgation are carried on to be clear both for citizens and for the local administrators or the sector companies. MatER is part of the Global WTERT (Waste to Energy Research & Technology) Council, international arena of excellences in the waste recovery research.
Public administrations, companies working in the waste sector. MatER aims to act as a bridge between university researchers, operators in the sector and agencies advancing solutions for sustainable waste recovery. The research carried out by MatER covers a wide range of connected sectors, from recycling to WTE incineration, from Mechanical Biological Treatment to anaerobic digestion, to the construction and modelling (through mass and energy balances, cost analyses and LCA) of integrated management scenarios.
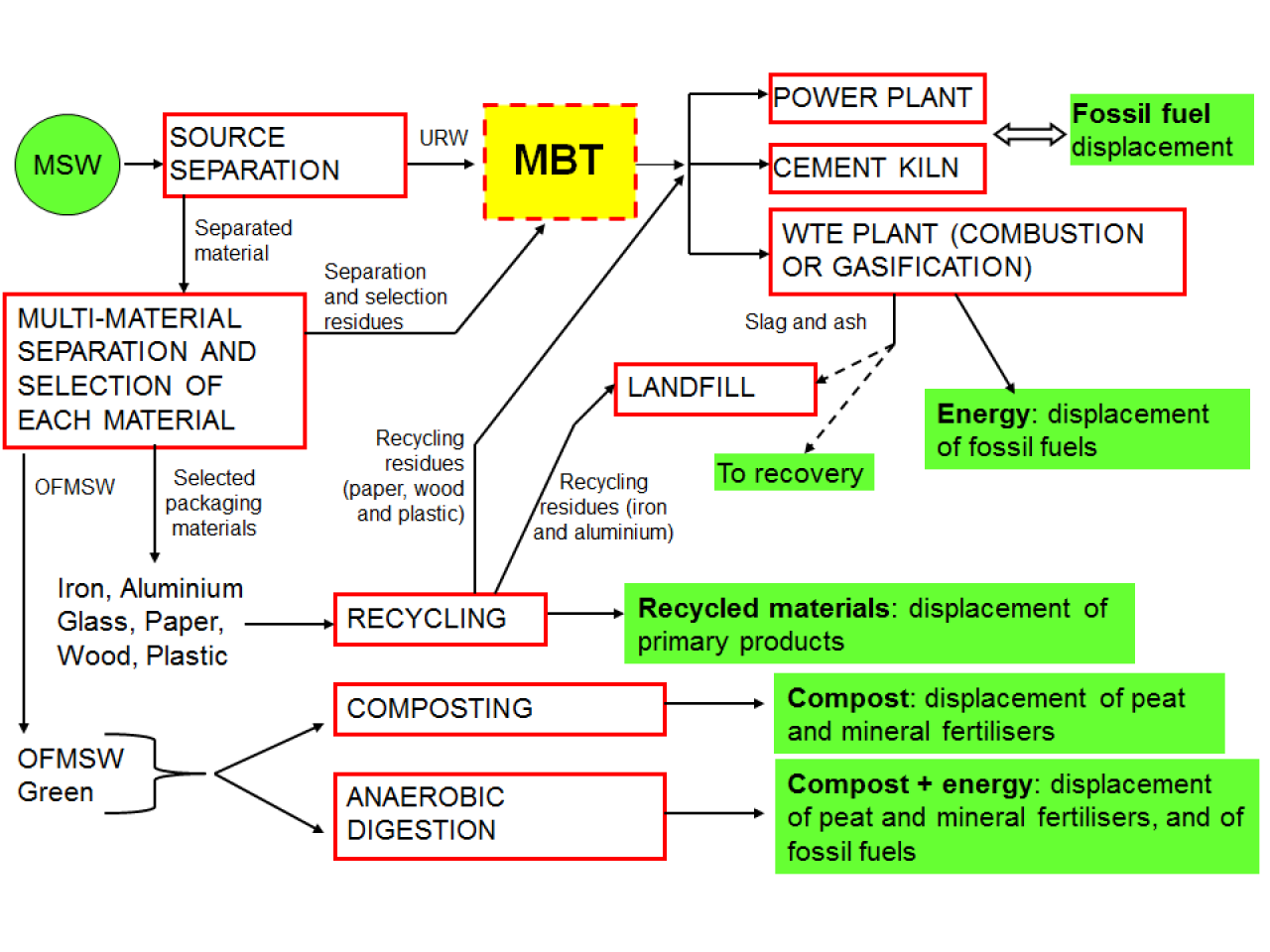 Possible recovery scenarios for an integrated waste management system
Possible recovery scenarios for an integrated waste management system
Scenarios for recovery and reuse of incineration plant and multi-material waste separate collection system by-products
The study focused on strategies for the treatment of the bottom ash from incineration plants (WtE) and of the glass residue from a multi-material collection process. The most well-established recovery sectors are the construction industry (cement and concrete) for WtE bottom ashes, and the ceramics and construction sector (tiles, stoneware) for waste glass, as well as recovery in glassworks like glass residues. Alternative recovery strategies for waste materials were compared (ashes from incineration and cullet), on the basis of a typical case (plant in Northern Italy). Two recovery scenarios were hypothesized and compared (mass balances and economic budgets) for both materials, which differ in the type of reuse of the inert waste fraction (processing for use in cement works or to produce concrete), both in Northern Italy, while in both cases the residues from glass sorting were sent to a recovery plant in Northern Italy which allows 100% of the handled material to be reused. The results of the processing scenarios were compared with those of landfill disposal of the materials as they are. In view of the results of the study, and on the basis of experimentation with mixtures of slag, cement, aggregates and additives for tile production, it is economically convenient to develop large scale processes with joint utilisation of these residues. It was highlighted that recovering the materials is at least 37% less expensive than landfill disposal. The disposal distance plays a key role: the further the plant, the higher overall disposal costs are. Glass recovery is more onerous than bottom ashes recovery, compared to landfill disposal, whose cost is quite low in view of the material's inert nature.
Polytechnic University of Milan (DICA - Civil and Environmental Engineering Department) Waste management multi-utility company operating in Northern Italy
Oral presentation at the symposium "Material and energy recovery from waste: from the Prin project to the MatER Centre for Studies", Rome, 29/02/2012
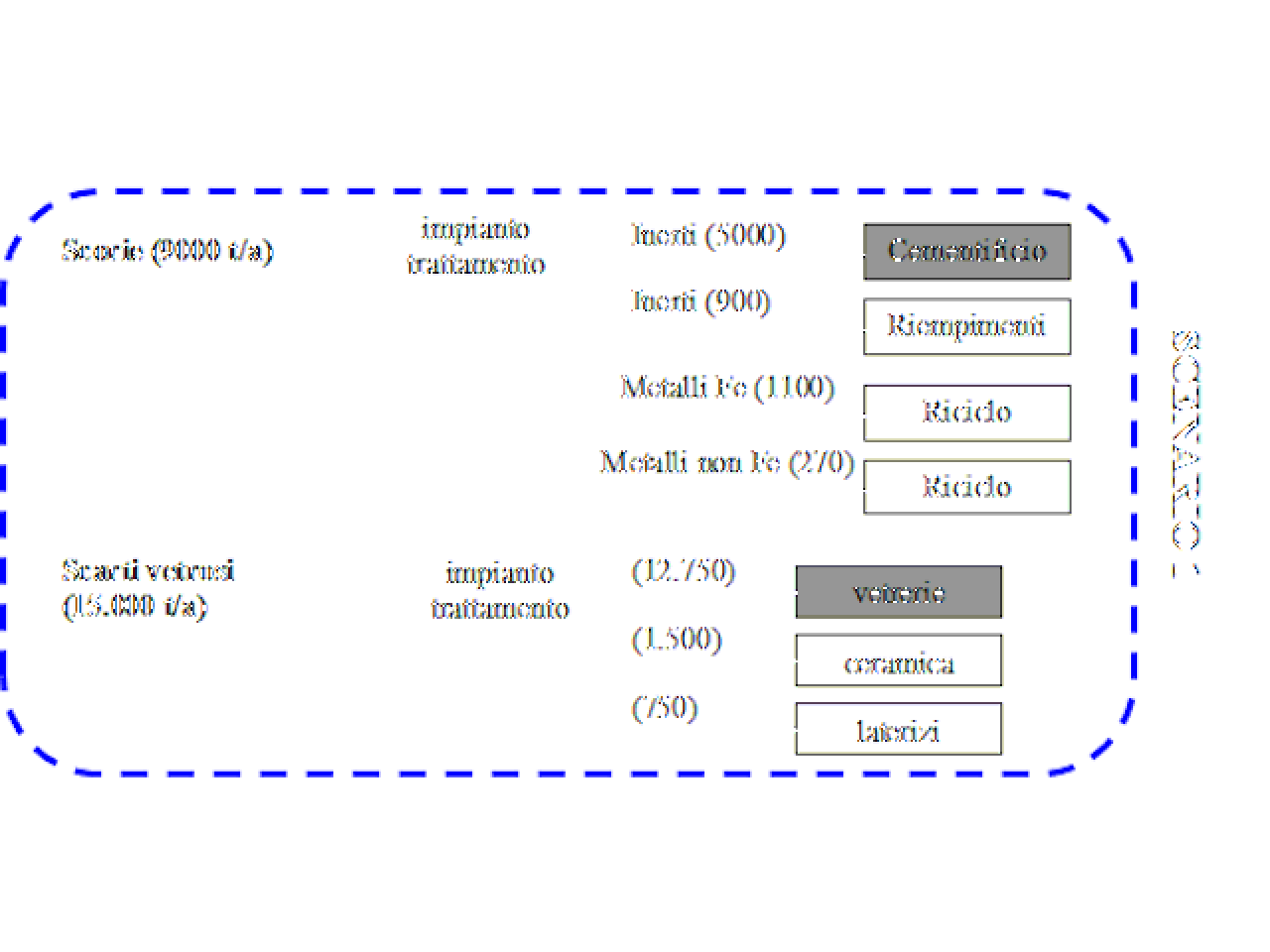 One of the bottom ashes and glass residues recovery scenarios in various processing plants surveyed
One of the bottom ashes and glass residues recovery scenarios in various processing plants surveyed

